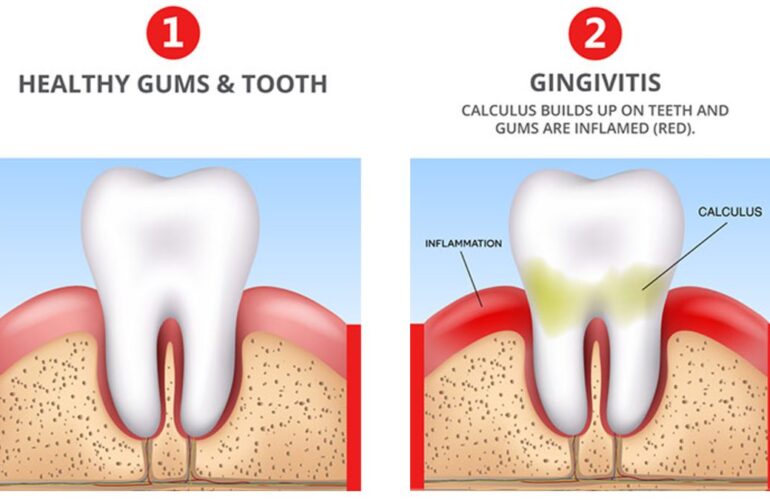
Periodontal disease is diagnosed by your dentist or periodontist (gum specialist) during your oral examination. A periodontal probe (small dental instrument) is gently used to measure the sulcus (pocket or space) between the tooth and the gums. Your dentist will use pocket depths, amount of bleeding, inflammation, tooth mobility, etc. to make a diagnosis of periodontal disease.
The main aim of treatment is to clean out bacteria from the pockets around the teeth and prevent further destruction of bone and tissue.
Nonsurgical treatments
If periodontitis isn’t advanced, treatment may involve less invasive procedures, including:
- Scaling. Scaling removes tartar and bacteria from your tooth surfaces and beneath your gums. It may be performed using instruments, a laser, or an ultrasonic device.
- Root planing. Root planing smooths the root surfaces, discouraging further buildup of tartar and bacteria.
- Antibiotics. Topical or oral antibiotics can help control bacterial infection.
Surgical treatments
If you have advanced periodontitis, treatment may require dental surgery, such as:
- Flap surgery (pocket reduction surgery). Your periodontist makes tiny incisions in your gum so that a section of gum tissue can be lifted back, exposing the roots for more effective scaling and root planing. After you heal, it’s easier to clean these areas and maintain healthy gum tissue.
- Soft tissue grafts. This procedure can help reduce further gum recession, cover exposed roots.
- Bone grafting. This procedure is performed when periodontitis has destroyed the bone surrounding your tooth root. The bone graft helps prevent tooth loss by holding your tooth in place.
- Guided tissue regeneration. This allows the regrowth of bone that was destroyed by bacteria. A special piece of biocompatible fabric is placed between the existing bone and your tooth. The material prevents unwanted tissue from entering the healing area, allowing bone to grow back instead.